Stress analysis of Airway stents
2012
---
1
•
Central
airway obstruction produces
symptoms of
dyspnea,
stridor,
and
obstructive pneumonia and is frequently
increases the morbidity and mortality rates.
•
Airway stents can improve pulmonary
function and the quality of life of patients.
•
The four main types of stents currently in use
are: silicone stent, balloon dilated metal
stent, self-expanding metal
stent and
covered self-expanding metal stent.
•
The major drawbacks of the four main
types of
stents currently in use are
formation necrosis of mucosa and fistula
formation due to radial forces.
•
Previous project investigated the effect of the
radial forces exerted by the different stents
on the airways. This project continues the
research.
1
.
Background
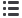
Stent insertion into an obstructed trachea
Student name:
Dikla Kesner
Department:
Medical Engineering
Advisor name:
Dr. Sara Naftali
Expanding the previous research by evaluating
the mechanical effect on various stents in
varied trachea models such as:
During different breathing pattern such as
coughing.
In different stenosis percent in the trachea.
2. Objectives
Numerical Technique
•
Geometrical model assembly:
SolidWorks 3D CAD.
•
Simulation package: Ansys 15.0.
•
Numerical simulation method: Finite
elements.
•
Stress simulation was performed by
using the “Shrink Fit” function.
•
Lagrazian, 3D mesh type, 6000-35000
tetrahedral elements with 4 nodes each.
Governing Equation
The static dynamic equation at steady
state:
Boundary Conditions
•
Zero displacement at the harnessed
edges of the trachea -radial movements
are available (inflating and shrinking).
•
For the simulation of cough - external
pressure of 6.6 Kpa applied on tracheal
contraction.
•
Overlapping interaction applied in the
stent-trachea contact.
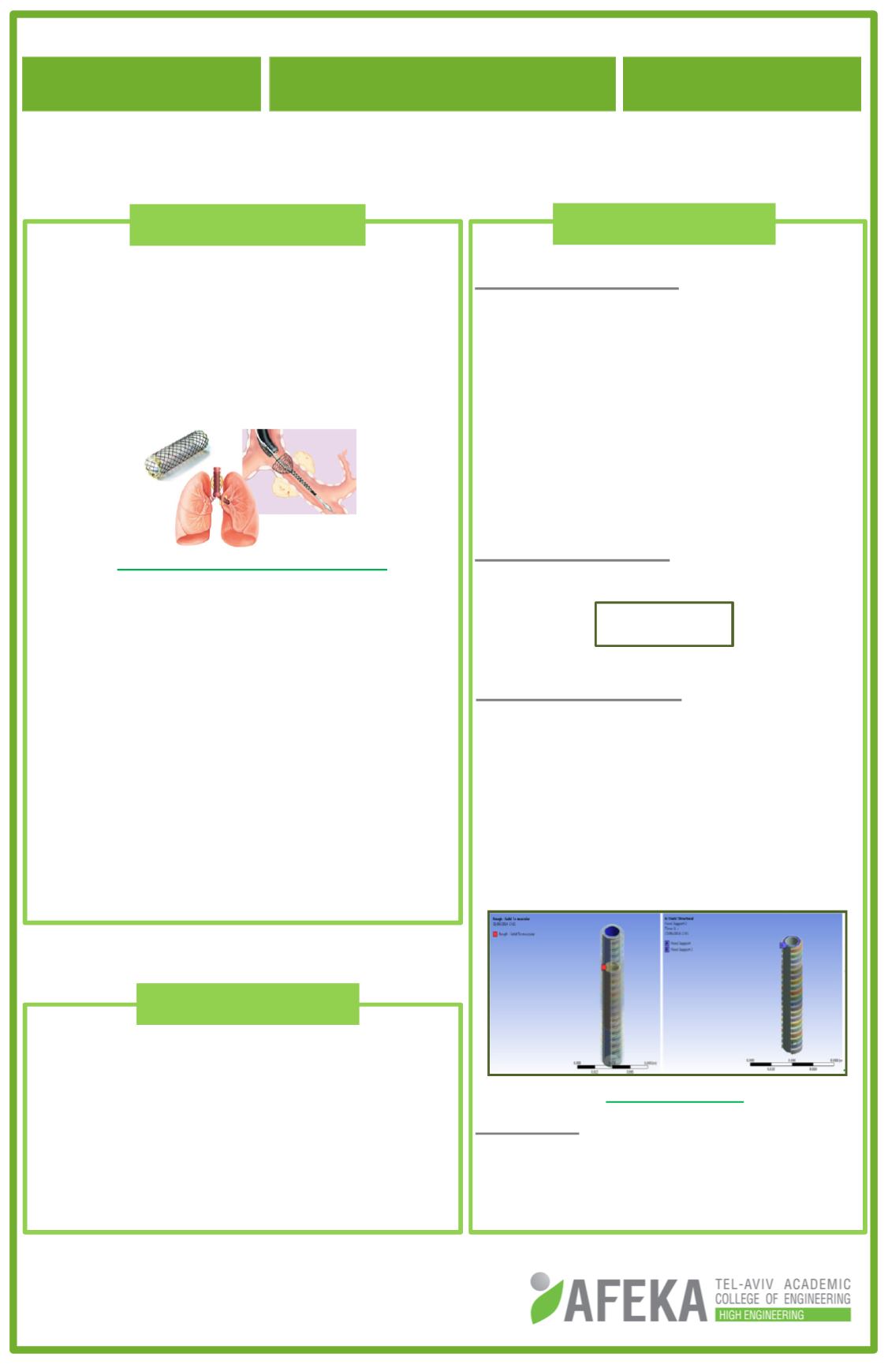
Geometry:
The trachea geometrical models consists
of two layers: cartilage rings and smooth
muscles with inner diameter
Boundary conditions
ku=F
3. Methods
u
- displacements,
k
- structure stiffness,
F
- external forces