2014
---
2
4.1. Numerical Model
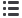
Stress distribution in the stump within BS
Different force angle in the BS model
The increased forced applied by the 45 [deg]
angle (walking), causes greater stress than the
vertical normal forces applied when standing.
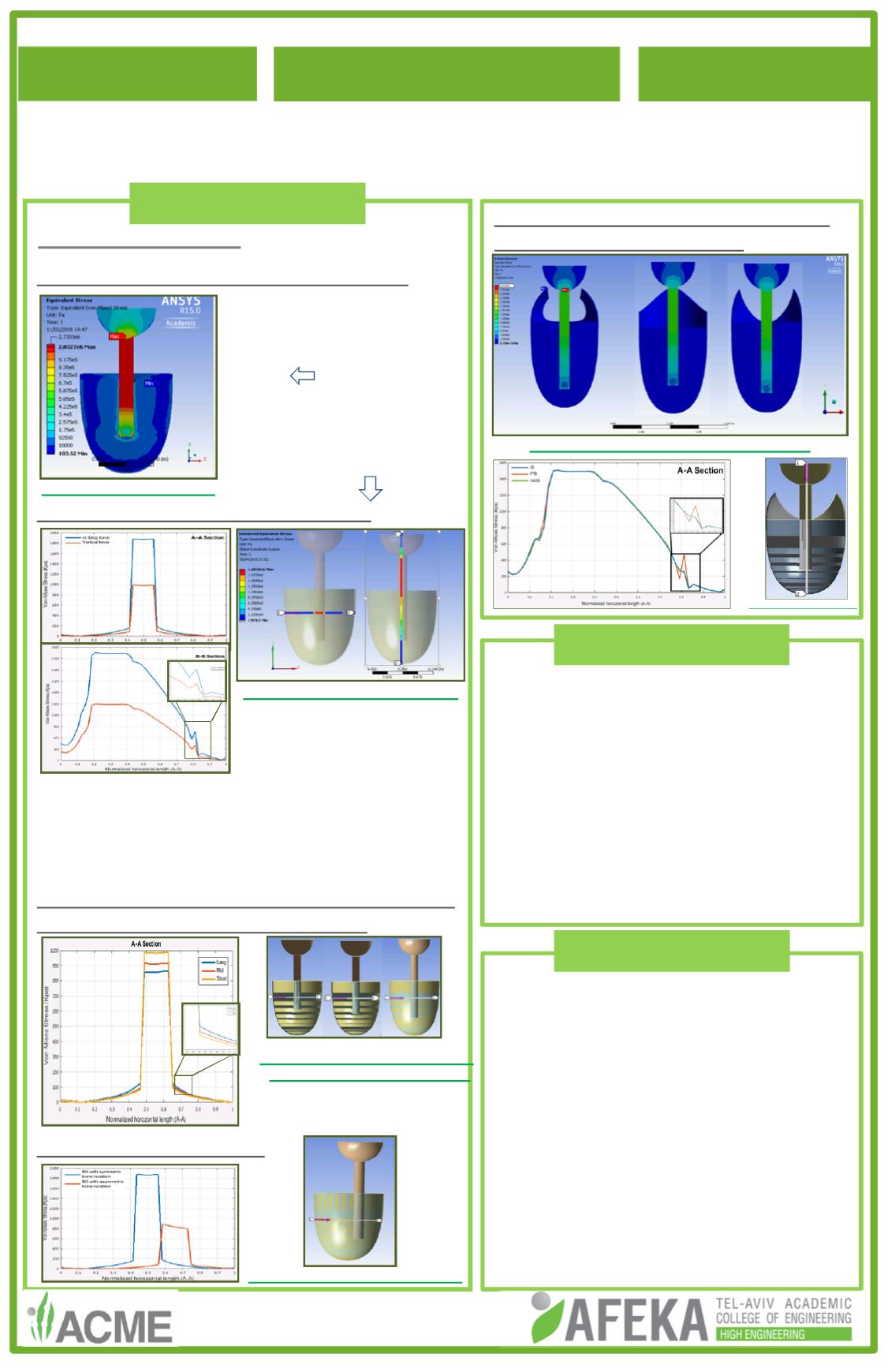
Different distance between the truncated bone
and the bottom of the stump with BS
Different bone’s locations
•
The obtained stress values are
correlated with the truncated bone
length.
•
The asymmetric bone location causes
lower stress distribution.
•
Stresses distribution in the stump with
PTB and 3S sockets are similar, and
Higher than with VASS socket.
•
Force in 45 [deg] causes greater
stresses than normal force.
Basic socket (BS) stresses
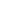
Stress distribution in the stump within
different trans-tibial sockets
•
Stresses are greater when walking on
both bone and soft tissue.
•
the maximum Von Mises stress value
was measured at the top of the tibial
bone, below the knee.
•
Asymmetric bone location causes
lower stress on the bone.
•
Longer tibia applies less stresses on
the bone.
•
VASS socket may reduce the risk of
deep tissue injury development in the
stump.
4
.
Results
5
.
Discussion
6
.
Conclusions
Short Mid Long
Different distance from the bone
end to the bottom of the stump
section -
A cross
-
S socket A
3
The highest stresses
distribution in the stump
soft tissue is along the
Tibia.
Profile data examined at
2 cross-sections:
horizontal (A-A) and
vertical (B-B).
Short bone causes high
stresses at A-A section.
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
A
B
Student name:
Guy Ateret
Department:
Medical Engineering
Advisor name:
Dr. Sara Naftali
Strains and stresses at sockets of
lower limbs - under the knee - prostheses
A
A
sections
-
Basic socket (BS) cross
sections
-
Asymmetric bone cross
PTB 3S
V
ASS
tibial socket types
-
Stress on different trans