Student name:
Guy Ateret
Department:
Medical Engineering
Advisor name:
Dr. Sara Naftali
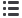
Strains and stresses at sockets of
lower limbs - under the knee - prostheses
2014
---
1
•
The main part of a prosthesis that effects
comfort and patient satisfaction is the socket. It
should provide suspension of prosthesis,
comfortable weight-bearing in the socket and
also protect the residual limb tissue.
•
The skin and soft tissue are not well adapted to
take loads during prosthetic gait. Therefore, a
not suitable socket can often cause heavy
tissue injuries.
•
There are three main types of socket interface
designs that are divided by their suitability to the
residual limb structure and weight bearing
characteristics: Patellar Tendon Bearing design
(PTB), Silicone Suction Suspension (3S), and
Vacuum Assisted Socket System (VASS)
.
•
Mechanical function comparison between the
three trans-tibial prosthetic sockets main types
has not been performed yet.
1
.
Background
To examine the developed strains and
stresses in 3D stump models with different
pathologies within basic socket designs,
using numerical method.
To compare between the mechanical function
of the three main types of the trans-tibial
prosthetic sockets in a stump model.
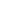
3.1. Numerical Model
Numerical Technique:
•
Geometrical model assembly:
SolidWorks 3D CAD
•
Simulation package: ANSYS 15.
•
Numerical simulation method: Finite
elements.
•
Meshing method: Lagrangian, with
150000-270000 linear tetrahedral
elements 4 nodes type.
Governing Equation
The static dynamic equation at steady-
state:
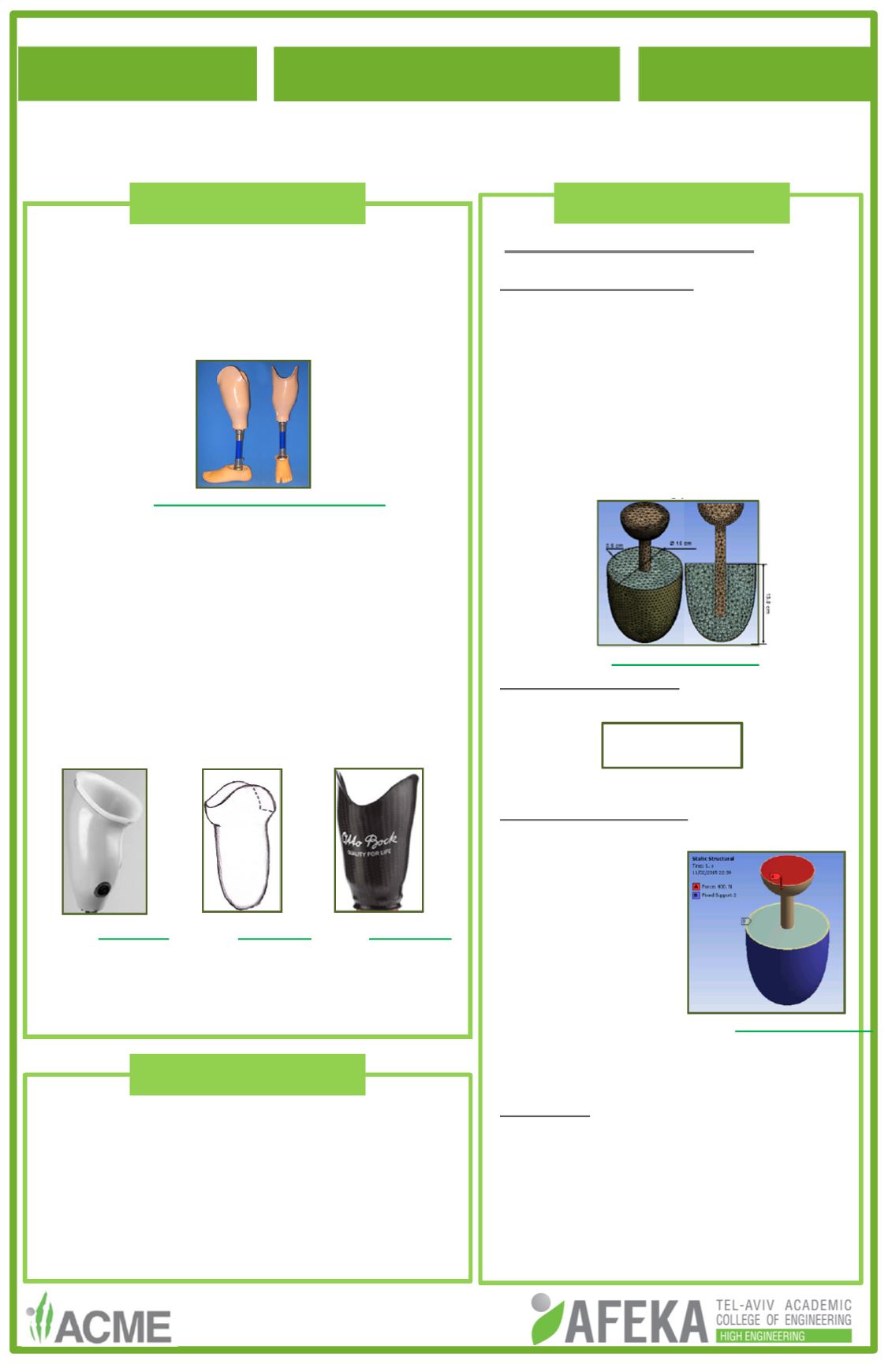
Boundary Conditions
•
The socket is fixed.
Geometry
Prosthesis for transtibial amputees.
VASS socket
PTB socket
S socket
3
Boundary conditions
3
.
Methods
2
.
Objectives
Ku=F
Mesh of a Basic model
•
The tibial bone’s
head is put under a
pre-load.
•
A load of 400N is
applied to the tibial
bone.
•
Overlapping
interaction applied
u
- displacements,
k
- structure stiffness,
F
- external forces
in the socket-stump contact.
•
Variety of stump models with different
pathologies (tightness, bone length
and asymmetric location) in Basic
socket (BS)
•
Three types of trans-femoral socket
interface designs